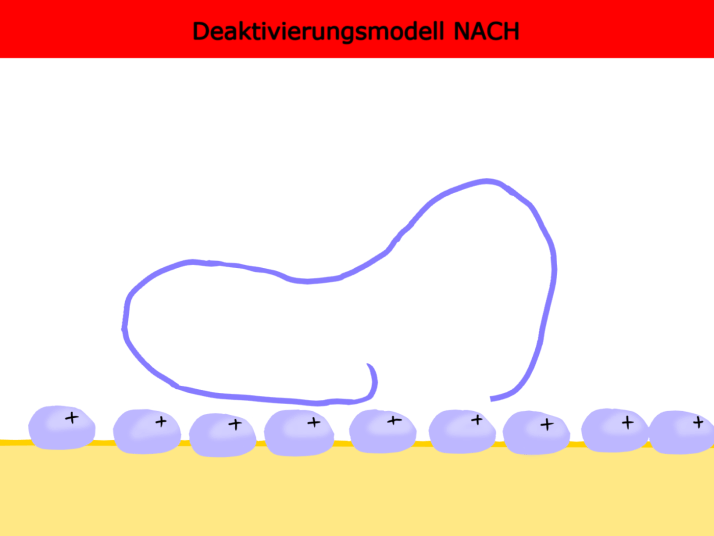
LITERATUR
und REFERNZEN^H.Lu et al. (2011). "Seed-mediated Plasmon-driven Regrowth of Silver Nanodecahedrons (NDs)". Plasmonics 7 (1): 167–173. doi:10.1007/s11468-011-9290-8.
^Stepanov, A. L.; Popok, V. N.; Hole, D. E. (2002). Glass Physics and Chemistry 28 (2): 90. doi:10.1023/A:1015377530708.
^ Magnetic antimicrobial nanocomposite based on bacterial cellulose and silver nanoparticles Manthiriyappan Sureshkumar, Dessy Yovita Siswanto and Cheng-Kang Lee, J. Mater. Chem., 2010, 20, 6948-6955.
^ Montazer, Majid; Farbod Alimohammadi, Ali Shamei, Mohammad Karim Rahimi (Jan 2012). "In situ synthesis of nano silver on cotton using Tollens’ reagent". Carbohydrate Polymers 87: 1706– 1712. doi:10.1016/j.carbpol.2011.09.079.
^ Samsung's Silver Nano Washer Ads Reportedly Exaggerated, Nov 21, 2005
^ Johnston HJ, Hutchison G, Christensen FM, Peters S, Hankin S, Stone V (April 2010). "A review of the in vivo and in vitro toxicity of silver and gold particulates: particle attributes and biological mechanisms responsible for the observed toxicity". Crit. Rev. Toxicol. 40 (4): 328–46. doi:10.3109/10408440903453074. PMID20128631.
^ Ahamed M, Alsalhi MS, Siddiqui MK (December 2010). "Silver nanoparticle applications and human health". Clin. Chim. Acta 411 (23–24): 1841–8. doi:10.1016/j.cca.2010.08.016. PMID20719239.
^ Qin, Yimin (2005). "Silver-containing alginate fibres and dressings". International Wound Journal 2 (2): 172–6. doi:10.1111/j.1742-4801.2005.00101.x. PMID16722867.
^ Hermans MH (2006). "Silver-containing dressings and the need for evidence". The American journal of nursing 106 (12): 60–8; quiz 68–9. doi:10.1097/00000446-200612000-00025. PMID17133010.
^ Chopra, I. (2007). "The increasing use of silver-based products as antimicrobial agents: a useful development or a cause for concern?". Journal of Antimicrobial Chemotherapy 59 (4): 587–90. doi:10.1093/jac/dkm006. PMID17307768.
^ a b Atiyeh BS, Costagliola M, Hayek SN, Dibo SA (2007). "Effect of silver on burn wound infection control and healing: review of the literature". Burns 33 (2): 139–48. doi:10.1016/j.burns.2006.06.010. PMID17137719.
^ Lansdown AB (2006). "Silver in health care: antimicrobial effects and safety in use". Current Problems in Dermatology 33: 17–34. doi:10.1159/000093928. PMID16766878.
^ Holmstrup, P (1991). "Reactions of the oral mucosa related to silver amalgam: a review". Journal of Oral Pathology & Medicine 20 (1): 1–7. PMID2002442.
^ Trop, Marji, Michael Novak, Siegfried Rodl, Bengt Hellbom, Wolfgang Kroell, and Walter Goeseeler (2006). "Silver-coated dressing acticaot caused raised liver enzymes and argyris-like symptoms in burn patient". The Journal of Trauma, Injury, Infection and Critical Care 60 (3): 648–652. doi:10.1097/01.ta.0000208126.22089.b6.
^ Parkes, A. (2006). "Silver-coated dressing Acticoat". Journal of Trauma-Injury Infection & Critical Care 61 (1): 239–40. doi:10.1097/01.ta.0000224131.40276.14.
^ Different sizes of colloidal gold particles.
^ Bernhard Wessling, Conductive Polymer / Solvent Systems: Solutions or Dispersions?, 1996 (on-line here)
^ University of Edinburgh School of Physics: Colloids (mentions Elixir of Life) 20.^ Paul Mulvaney, University of Melbourne, The beauty and elegance of Nanocrystals, Use since Roman times
^ C. N. Ramachandra Rao, Giridhar U. Kulkarni, P. John Thomasa, Peter P. Edwards, Metal nanoparticles and their assemblies, Chem. Soc. Rev., 2000, 29, 27-35. (on-line here; mentions Cassius and Kunchel)
^ S.Zeng et al. (2011). "A review on functionalized gold nanoparticles for biosensing applications". Plasmonics 6 (3): 491-506. doi:10.1007/s11468-011-9228-1.
^ a b Sharma, Vivek; Park, Kyoungweon; Srinivasarao, Mohan (2009). "Colloidal dispersion of gold nanorods: Historical background, optical properties, seed-mediated synthesis, shape separation and self-assembly". Material Science and Engineering Reports 65 (1–3): 1–38. doi:10.1016/j.mser.2009.02.002.
^ a b V. R. Reddy, "Gold Nanoparticles: Synthesis and Applications" 2006, 1791, and references therein
^ Michael Faraday, Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society, London, 1857
^ Gay-Lussac (1832). "Ueber den Cassius'schen Goldpurpur". Annalen der Physik 101 (8): 629–630. Bibcode 1832AnP...101..629G. doi:10.1002/andp.18321010809.
^ Berzelius, J. J. (1831). "Ueber den Cassius' schen Goldpurpur". Annalen der Physik 98 (6): 306–308. Bibcode 1831AnP....98..306B. doi:10.1002/andp.18310980613.
^ Faraday, M. (1857). "Experimental Relations of Gold (and Other Metals) to Light,". Philos. Trans. R. Soc. London 147: 145. doi:10.1098/rstl.1857.0011.
^ Zsigmondy, Richard (December 11, 1926). "Properties of colloids". Nobel Foundation. Retrieved 2009
^ S.Zeng et al. (2012). "Size dependence of Au NP-enhanced surface plasmon resonance based on differential phase measurement". Sensors and Actuators B: Chemical. doi:10.1016/j.snb.2012.09.073.
^ J. Turkevich, P. C. Stevenson, J. Hillier, "A study of the nucleation and growth processes in the synthesis of colloidal gold", Discuss. Faraday. Soc. 1951, 11, 55-75.
^ J. Kimling, M. Maier, B. Okenve, V. Kotaidis, H. Ballot, A. Plech, "Turkevich Method for Gold Nanoparticle Synthesis Revisited", J. Phys. Chem. B 2006, 110, 15700-15707.
^ a b G. Frens, "Particle size and sol stability in metal colloids", Colloid & Polymer Science 1972, 250, 736-741.
^ a b G. Frens, "Controlled nucleation for the regulation of the particle size in monodisperse gold suspensions", Nature (London), Phys. Sci. 1973, 241, 20-22.
^ BK Pong et al. J. Phys. Chem. C, 111 (17), 6281 -6287, 2007. New Insights on the Nanoparticle Growth Mechanism in the Citrate Reduction of Gold(III) Salt: Formation of the Au Nanowire Intermediate and Its Nonlinear Optical Properties
^ M. Brust; M. Walker; D. Bethell; D. J. Schiffrin; R. Whyman (1994). "Synthesis of Thiol-derivatised Gold Nanoparticles in a Two-phase Liquid-Liquid System". Chem. Commun. (7): 801. doi:10.1039/C39940000801.
^ Manna, A.; Chen, P.; Akiyama, H.; Wei, T.; Tamada, K.; Knoll, W. (2003). "Optimized Photoisomerization on Gold Nanoparticles Capped by Unsymmetrical Azobenzene Disulfides". Chem. Mater. 15 (1): 20–28. doi:10.1021/cm0207696.
^ S.D. Perrault; W.C.W. Chan (2009). "Synthesis and Surface Modification of Highly Monodispersed, Spherical Gold Nanoparticles of 50-200 nm". J. Am. Chem. Soc. 131 (47): 17042–3. doi:10.1021/ja907069u. PMID19891442.
^ Jianling Zhang; Jimin Du; Buxing Han; Zhimin Liu; Tao Jiang; Zhaofu Zhang (2006). "Sonochemical Formation of Single-Crystalline Gold Nanobelts". Angew. Chem. 118 (7): 1134–7. doi:10.1002/ange.200503762.
^ "Colloidal gold, a useful marker for transmission and scanning electron microscopy" by M Horisberger Journal of Histochemistry and Cytochemistry Volume 25, Issue 4, pp. 295-305, 04/01/1977 [1] "
^Staphylococcal protein a bound to colloidal gold: A useful reagent to label antigen-antibody sites in electron microscopy", by Egidio L Romanoa and Mirtha Romanoa. Immunochemistry Volume 14, Issues 9-10, September–October 1977, Pages 711-715, doi:10.1016/0019 2791(77)90146-X
^ Simultaneous visualization of chromosome bands and hybridization signal using colloidal-gold labeling in electron microscopy [2]
^ Double labeling with colloidal gold particles of different sizes
^ Amelioration of collagen-induced arthritis in rats by nanogold.
^ "BMJ case reports: Chrysiasis"
^ Drug Reference for EMS Providers, Richard K.Beck, 2002, pages 164-165: auranofin and Aurothioglucose side effects & overdose
^ Auranofin complete list of warnings,precautions and reactions various inflammations
^ Aurothioglucose Suspension adverse:
^ Gold sodium thiomalate: adverse effects including allergy to gold, tolerance to gold decreasing with age, skin and renal complications.
^ Therapeutic possibilities of plasmonically heated gold nanoparticles.
^ Paclitaxel-Functionalized Gold Nanoparticles Jacob D. Gibson, Bishnu P. Khanal, and Eugene R. Zubarev J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2007, 129, 11653-11661 doi:10.1021/ja075181k
^ Qian, Ximei. "In vivo tumor targeting and spectroscopic detection with surface-enhanced Raman nanoparticle tags." Nature Biotechnology. 2008. Vol 26 No 1.
^ Hainfeld, James et al. "The use of gold nanoparticles to enhance radiotherapy in mice." Phys. Med. Biol. 2004. Vol 49 N309-315
^ McMahon, Stephen et al. "Biological consequences of nanoscale energy deposition near irradiated heavy atom nanoparticles." Nature Scientific Reports
^ Guo T, Nikolaev P, Rinzler D, Tomanek DT, Colbert DT, Smalley RE (1995). "Self-Assembly of Tubular Fullerenes". J. Phys. Chem. 99 (27): 10694–7. doi:10.1021/j100027a002.
^ Guo T, Nikolaev P, Thess A, Colbert DT, Smalley RE (1995). "Catalytic growth of single-walled nanotubes by laser vaporization". Chem. Phys. Let. 243: 49. Bibcode 1995CPL...243...49B. doi:10.1016/0009-2614(95)00825-O.
^ Robert Eason - Pulsed Laser Deposition of Thin Films: Applications-Led Growth of Functional Materials Wiley-Interscience | 2006 | ISBN: 0471447099
^ Kuang S, Doran SA, Wilson RJ, Goss GG, Goldberg JI (2002). "Serotonergic sensory-motor neurons mediate a behavioral response to hypoxia in pond snail embryos". J. Neurobiol. 52 (1): 73–83. doi:10.1002/neu.10071. PMID12115895.
^ Valcavi R, Riganti F, Bertani A, Formisano D, Pacella CM. (2010). "Percutaneous Laser Ablation of Cold Benign Thyroid Nodules: A 3-Year Follow-Up Study in 122 Patients". Thyroid. 20:11.
^ Pacella CM , Francica G , Di Lascio FM , Arienti V , Antico E , Caspani B , Magnolfi F , Megna AS , Pretolani S , Regine R , Sponza M , Stasi R . (giugno 2009). "Long-term outcome of cirrhotic patients with early hepatocellular carcinoma treated with ultrasound-guided percutaneous laser ablation: a retrospective analysis". J Cli
https://nanobeauty.pl